
“I began my blockchain journey looking for a network that would actually allow real businesses to create solutions on decentralized networks, but the product simply didn’t exist,” said Tal Kol, Orbs Co-Founder and technical lead.
“With the launch of Orbs, developers and businesses finally have a system that will enable them to build game changing solutions on the blockchain. It allows a fundamental shift from building for the sake of the movement alone, to building products that can drive immediate impact.”
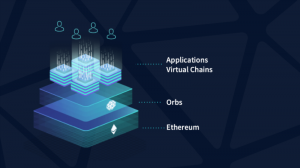
The Orbs environment
The Orbs environment includes a stack of tools capable of creating real solutions on a blockchain. This includes:
- lean helix consensus – a randomised proof of stake algorithm which enables high performance alongside large scale decentralisation
- polyglot smart contracts – the ability to code smart contracts in both Go and Javascript (Orbs says more languages will come)
- full Ethereum interoperability – this serves as a performance layer alongside Ethereum’s trust layer
- a complete developer stack – end to end developer tools include a Contract SDK with full documentation, backend experimentation, testing framework, virtual chain production tools and an SDK for developing clients in Go, JavaScript and Python
- virtual chains are a core element in the Orbs architecture and is in V1 – the network can run multiple virtual chains in parallel on the same physical nodes (virtual chains provide isolation between apps and allow every app to make its own governance decisions)
- the PoS incentive model in V1 focuses on taking responsible steps towards permissionless governance – the first app running on top of Orbs is a virtual chain for PoS voting (it will allow token holders to elect validators for the permissionless validator pool).
The importance of virtual chains is that these:
- provide the feel and benefit of a dedicated blockchain
- run on top of a shared physical node infrastructure
- enjoy the security and decentralisation provided by the shared environment as well as the isolation and customisation provided by virtualisation
Consensus on transactions across different virtual chains can run independently and concurrently on separate resources. The ledgers of virtual chains can be maintained independently, with computation performed in parallel. It appears that the isolation of state for each virtual chain reduces the memory requirements of its virtual machine which, overall, offers advantages:
- each app operates its own virtual chain with inherent sharding
- app developers choose their virtual chain’s consensus protocol and governance model
- there is autonomous governance and flexibility
- isolation from congestion exists in other virtual chains
- there is an ability to start with a private instance and later switch to public – without having to migrate blockchains.
“From the day we began, our goal was to create a blockchain that would actually enable real solutions without sacrificing from decentralization,” said Daniel Peled, Co-Founder and President of Orbs. “The launch is a major step in this process and we look forward to bringing developers and businesses the support and product to maximize the potential of the technology.”
Fully open source

As stated in its original positioning paper, Orbs has always intended to be an open source project. The entire Orbs codebase — >60 repositories — is being made public on GitHub. The Orbs approach is that open source code should not restrict usage, which is why it has adopted the MIT licence (one of the more permissive ones).
This has some significant implications:
- anyone can start reviewing the system and audit what was built so far (Orbs believe external reviews are critical for meeting the target of a stable and secure system)
- anyone can fork and make their own versions of what Orbs has built (the IP will belong to the user community so that projects aspiring to decentralisation are accessible to everyone)
- external contributors can join and take part in the Orbs ecosystem (this ecosystem aims yo bring in external developers to start using V1 and to report issues, propose solutions and even implement some of these solutions).
Enterprise Times: what does this mean
The system Orbs is building has developers as its target audience. It is aiming for at least 99.999% stability for developer infrastructure (to be at least equivalent to established cloud services like AWS) though, as it says: “Are we there now? Of course, not”.
In order to keep the ORBS token, and the voting process, safe Orbs is relying on Ethereum. This should allow Orbs to learn in production – while minimising risks to token holders. While Orbs does currently provide a node which runs in ‘audit mode’ – to verify the output of the network without participating actively in the consensus – it sees value in adding such functionality. It says it plans to offer it in ‘upcoming months’.
The objectives of Orbs look and sound good. The need for development and tools support for blockchain are definitely a requirement. From this viewpoint, never mind the decentralisation capabilities described, Orbs should interest enterprises.

























